Ice is vital to many industries, from food and beverage to healthcare and construction. Businesses rely on a constant supply of ice to keep their products fresh, their equipment running smoothly, and their customers happy. While many types of ice are available, tube ice has emerged as a popular choice for many businesses due to its unique properties and ease of production. This article will explore the science behind tube ice production and how it can benefit your business.
The Basic of Tube Ice Making
Tube ice with a hole in the center. It is produced by freezing water around a tube, which is removed to create the hollow center. This differs from other types of ice, such as block ice or flake ice, which are formed by freezing water in a solid mass or by shaving chips off a larger block of ice.
The process of ice nucleation is crucial to the production of tube ice. Ice nucleation is the process by which a liquid transforms into a solid, and it occurs when a small particle, such as dust or bacteria, acts as a nucleus around which ice crystals can form. In tube ice making, ice nucleation is controlled by introducing a small amount of water to the tube, which acts as a nucleus for the ice crystals to grow around.
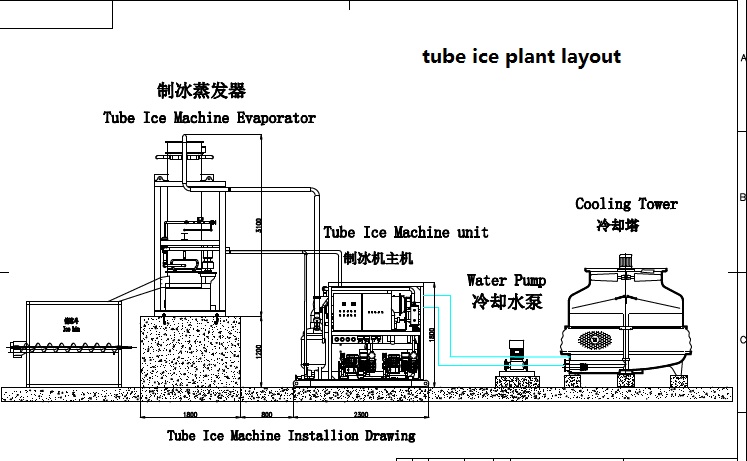
The Tube Ice-Making Process in Detail
The tube ice making process involves several steps, each of which is critical to the production of high-quality ice. The first step is to fill the evaporator with water, which is then frozen by a refrigeration system. The evaporator is a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, with the tubes acting as molds for the ice. As the water freezes, it adheres to the tubes and forms a layer of ice around them.
Once the ice has formed, it is harvested by a cutter, which cuts it into tubes of the desired length. The tubes are then removed from the evaporator and sent to a storage bin, where they are stored until needed.
The Science Behind Tube Ice Production
The science behind tube ice production is based on thermodynamics and heat transfer principles. Thermodynamics is the study of heat and energy, and it plays a crucial role in freezing water into ice. Heat transfer is the process by which heat is transferred from one object to another, and it is essential for maintaining the proper temperature in the tube ice machine.
The design of a tube ice machine can also impact the efficiency and quality of the ice produced. The size and shape of the evaporator, the type of refrigeration system used, and the placement of the cutter all play a role in determining the final product.
Proper maintenance and calibration of the tube ice machine are also critical for achieving optimal ice production. Regular cleaning and inspection can help prevent clogs and ensure the machine operates at peak efficiency.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the science behind tube ice production is fascinating and complex. Understanding the principles of ice nucleation, thermodynamics, and heat transfer can help businesses optimize their ice production and improve the quality of their products. Whether you are in the food and beverage industry, healthcare, or construction, tube ice can provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for your ice needs. To learn more about tube ice machines and how they can benefit your business, explore our website or contact us today to speak with one of our experts.
